Tool Calling
Tool calling(也称为 function calling)是 AI 应用程序中的常见模式,允许 model 与一组 API 或 tools 交互,增强其能力。
Tools 主要用于:
- 信息检索。此类别中的 tools 可用于从外部源检索信息,例如数据库、Web 服务、文件系统或 Web 搜索引擎。目标是增强 model 的知识,使其能够回答原本无法回答的问题。因此,它们可以在 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) 场景中使用。例如,可以使用 tool 检索给定位置的当前天气、检索最新新闻文章或查询数据库中的特定记录。
- 执行操作。此类别中的 tools 可用于在软件系统中执行操作,例如发送电子邮件、在数据库中创建新记录、提交表单或触发工作流。目标是自动化原本需要人工干预或显式编程的任务。例如,可以使用 tool 为与聊天机器人交互的客户预订航班、填写网页上的表单,或在代码生成场景中基于自动化测试(TDD)实现 Java 类。
尽管我们通常将 tool calling 称为 model 能力,但实际上由客户端应用程序提供 tool calling 逻辑。Model 只能请求 tool call 并提供输入参数,而应用程序负责从输入参数执行 tool call 并返回结果。Model 永远无法访问作为 tools 提供的任何 API,这是一个关键的安全考虑。
Spring AI 提供了便捷的 API 来定义 tools、解析来自 model 的 tool call 请求并执行 tool calls。以下部分概述了 Spring AI 中的 tool calling 功能。
NOTE: 请检查 Chat Model 比较 以查看哪些 AI model 支持 tool calling 调用。
TIP: 遵循指南从已弃用的 FunctionCallback 迁移到 ToolCallback API。
快速开始
让我们看看如何在 Spring AI 中开始使用 tool calling。我们将实现两个简单的 tools:一个用于信息检索,一个用于执行操作。信息检索 tool 将用于获取用户时区的当前日期和时间。操作 tool 将用于在指定时间设置闹钟。
信息检索
AI model 无法访问实时信息。任何假设了解当前日期或天气预报等信息的问题都无法由 model 回答。但是,我们可以提供一个可以检索此信息的 tool,并让 model 在需要访问实时信息时调用此 tool。
让我们在 DateTimeTools 类中实现一个 tool 来获取用户时区的当前日期和时间。该 tool 不接受任何参数。来自 Spring Framework 的 LocaleContextHolder 可以提供用户的时区。该 tool 将定义为用 @Tool 注解的方法。为了帮助 model 理解是否以及何时调用此 tool,我们将提供该 tool 功能的详细描述。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}
接下来,让我们使 tool 可用于 model。在此示例中,我们将使用 ChatClient 与 model 交互。我们将通过 tools() 方法传递 DateTimeTools 的实例来向 model 提供 tool。当 model 需要知道当前日期和时间时,它将请求调用 tool。在内部,ChatClient 将调用 tool 并将结果返回给 model,然后 model 将使用 tool call 结果生成对原始问题的最终响应。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);
输出将类似于:
Tomorrow is 2015-10-21.
您可以再次重试询问相同的问题。这次,不要向 model 提供 tool。输出将类似于:
I am an AI and do not have access to real-time information. Please provide the current date so I can accurately determine what day tomorrow will be.
没有 tool,model 不知道如何回答问题,因为它无法确定当前日期和时间。
执行操作
AI model 可用于生成完成某些目标的计划。例如,model 可以生成预订前往丹麦旅行的计划。但是,model 无法执行计划。这就是 tools 的用武之地:它们可用于执行 model 生成的计划。
在前面的示例中,我们使用 tool 来确定当前日期和时间。在此示例中,我们将定义一个用于在特定时间设置闹钟的第二个 tool。目标是从现在起 10 分钟设置闹钟,因此我们需要向 model 提供两个 tools 来完成此任务。
我们将新 tool 添加到与之前相同的 DateTimeTools 类中。新 tool 将接受单个参数,即 ISO-8601 格式的时间。然后,tool 将向控制台打印一条消息,指示已为给定时间设置闹钟。与之前一样,tool 定义为用 @Tool 注解的方法,我们还使用它提供详细描述以帮助 model 理解何时以及如何使用 tool。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time, provided in ISO-8601 format")
void setAlarm(String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
接下来,让我们使两个 tools 都可用于 model。我们将使用 ChatClient 与 model 交互。我们将通过 tools() 方法传递 DateTimeTools 的实例来向 model 提供 tools。当我们要求从现在起 10 分钟设置闹钟时,model 首先需要知道当前日期和时间。然后,它将使用当前日期和时间来计算闹钟时间。最后,它将使用闹钟 tool 来设置闹钟。在内部,ChatClient 将处理来自 model 的任何 tool call 请求,并将任何 tool call 执行结果发送回 model,以便 model 可以生成最终响应。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Can you set an alarm 10 minutes from now?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);
在应用程序日志中,您可以检查闹钟是否已在正确时间设置。
概述
Spring AI 通过一组灵活的抽象支持 tool calling,允许您以一致的方式定义、解析和执行 tools。本节概述了 Spring AI 中 tool calling 的主要概念和组件。
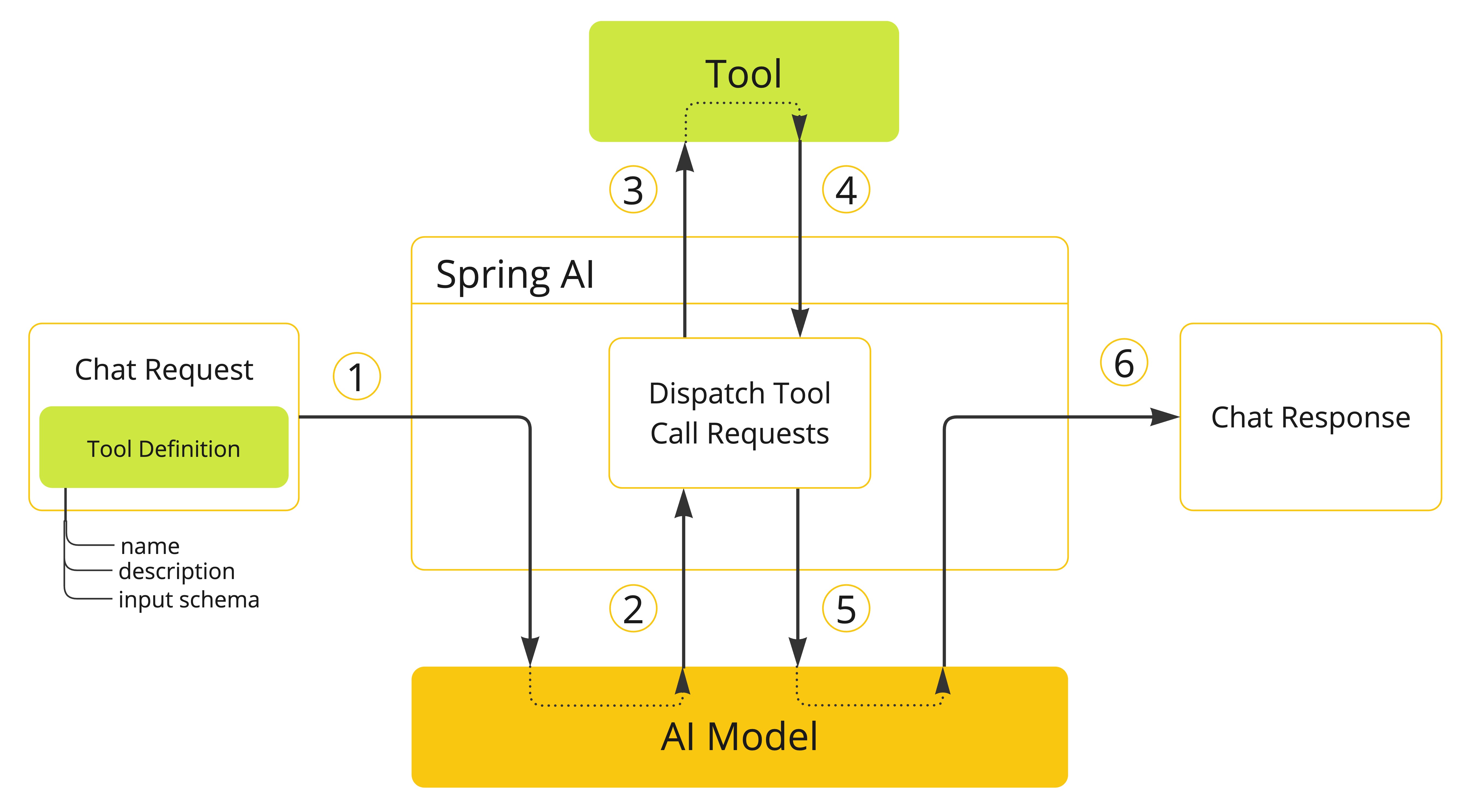
- 当我们想要使 tool 可用于 model 时,我们在聊天请求中包含其定义。每个 tool 定义包括名称、描述和输入参数的 schema。
- 当 model 决定调用 tool 时,它发送带有 tool 名称和根据定义 schema 建模的输入参数的响应。
- 应用程序负责使用 tool 名称来识别并使用提供的输入参数执行 tool。
- Tool call 的结果由应用程序处理。
- 应用程序将 tool call 结果发送回 model。
- Model 使用 tool call 结果作为附加上下文生成最终响应。
Tools 是 tool calling 的构建块,它们由 ToolCallback 接口建模。Spring AI 提供了从方法和函数指定 ToolCallback(s) 的内置支持,但您始终可以定义自己的 ToolCallback 实现以支持更多用例。
ChatModel 实现透明地将 tool call 请求分派到相应的 ToolCallback 实现,并将 tool call 结果发送回 model,最终生成最终响应。它们使用 ToolCallingManager 接口来执行此操作,该接口负责管理 tool 执行生命周期。
ChatClient 和 ChatModel 都接受 ToolCallback 对象列表,以使 tools 可用于 model 和最终执行它们的 ToolCallingManager。
除了直接传递 ToolCallback 对象外,您还可以传递 tool 名称列表,这些名称将使用 ToolCallbackResolver 接口动态解析。
以下部��分将更详细地介绍所有这些概念和 API,包括如何自定义和扩展它们以支持更多用例。
方法作为 Tools
Spring AI 提供了两种从方法指定 tools(即 ToolCallback(s))的内置支持:
- 声明式,使用
@Tool注解 - 编程式,使用低级
MethodToolCallback实现。
声明式规范:@Tool
您可以通过用 @Tool 注解方法来将方法转换为 tool。
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}
@Tool 注解允许您提供有关 tool 的关键信息:
name:tool 的名称。如果未提供,将使用方法名称。AI model 使用此名称在调用时识别 tool。因此,不允许在同一类中有两个同名 tools。名称必须在特定聊天请求中提供给 model 的所有 tools 中唯一。description:tool 的描述,model 可以使用它来理解何时以及如何调用 tool。如果未提供,方法名称将用作 tool 描述。但是,强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对于 model 理解 tool 的用途以及如何使用它至关重要。未能提供良好的描述可能导致 model 在应该使用时不使用 tool 或错误使用它。returnDirect:tool 结果是否应直接返回给客户端或传递回 model。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 返回直接。resultConverter:用于将 tool call 的结果转换为String object以发送回 AI model 的ToolCallResultConverter实现。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 结果转换。
方法可以是静态的或实例的,并且可以具有任何可见性(public、protected、package-private 或 private)。包含方法的类可以是顶级类或嵌套类,也可以具有任何可见性(只要在您计划实例化它的地方可以访问)。
NOTE: Spring AI 为
@Tool注解方法的 AOT 编译提供内置支持,只要包含方法的类是 Spring bean(例如@Component)。否则,您需要向 GraalVM 编译器提供必要的配置。例如,通过用@RegisterReflection(memberCategories = MemberCategory.INVOKE_DECLARED_METHODS)注解类。
您可以为方法定义任意数量的参数(包括无参数),支持大多数类型(基元、POJO、枚举、列表、数组、映射等)。同样,方法可以返回大多数类型,包括 void。如果方法返回值,返回类型必须是可序列化类型,因为结果将被序列化并发送回 model。
NOTE: 某些类型不受支持。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 方法 Tool 限制。
Spring AI 将自动为 @Tool 注解方法的输入参数生成 JSON schema。Schema 由 model 用于理解如何调用 tool 并准备 tool 请求。@ToolParam 注解可用于提供有关输入参数的附加信息,例如描述或参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有输入参数都被视为必需。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
@ToolParam 注解允许您提供有关 tool 参数��的关键信息:
description:参数的描述,model 可以使用它来更好地理解如何使用它。例如,参数应该是什么格式,允许什么值等。required:参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有参数都被视为必需。
如果参数用 @Nullable 注解,除非使用 @ToolParam 注解明确标记为必需,否则将被视为可选。
除了 @ToolParam 注解外,您还可以使用来自 Swagger 的 @Schema 注解或来自 Jackson 的 @JsonProperty。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 JSON Schema。
向 ChatClient 添加 Tools
使用声明式规范方法时,您可以在调用 ChatClient 时将 tool 类实例传递给 tools() 方法。此类 tools 仅适用于添加它们的特定聊天请求。
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();
在底层,ChatClient 将从 tool 类实例中的每个 @Tool 注解方法生成 ToolCallback,并将它们传递给 model。如果您希望自己生成 ToolCallback(s),可以使用 ToolCallbacks 实用类。
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
向 ChatClient 添加默认 Tools
使用声明式规范方法时,您可以通过将 tool 类实例传递给 defaultTools() 方法,将默认 tools 添加到 ChatClient.Builder。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在从同一
ChatClient.Builder构建的所有ChatClient实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(new DateTimeTools())
.build();
向 ChatModel 添加 Tools
使用声明式规范方法时,您可以将 tool 类实例传递给用于调用 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 toolCallbacks() 方法。此类 tools 仅适用于添加它们的特定聊天请求。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(dateTimeTools)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What day is tomorrow?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);
向 ChatModel 添加默认 Tools
使用声明式规范方法时,您可以通过将 tool 类实例传递给用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolCallbacks() 方法,在构造时向 ChatModel 添加默认 tools。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在该
ChatModel实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ToolCallback[] dateTimeTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(dateTimeTools)
.build())
.build();
编程式规范:MethodToolCallback
您可以通过编程方式构建 MethodToolCallback 来将方法转换为 tool。
class DateTimeTools {
String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}
MethodToolCallback.Builder 允许您构建 MethodToolCallback 实例并提供有关 tool 的关键信息:
toolDefinition:定义 tool 名称、描述和输入 schema 的ToolDefinition实例。您可以使用ToolDefinition.Builder类构建它。必需。toolMetadata:定义附加设置的ToolMetadata实例,例如结果是否应直接返回给客户端,以及要使用的结果转换器。您可以使用ToolMetadata.Builder类构建它。toolMethod:表示 tool 方法的Method实例。必需。toolObject:包含 tool 方法的对象实例。如果方法是静态的,您可以省略此参数。toolCallResultConverter:用于将 tool call 的结果转换为String对象以发送回 AI model 的ToolCallResultConverter实例。如果未提供,将使用默认转换器(DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
ToolDefinition.Builder 允许您构建 ToolDefinition 实例并定义 tool 名称、描述和输入 schema:
name:tool 的名称。如果未提供,将使用方法名称。AI model 使用此名称在调用时识别 tool。因此,不允许在同一类中有两个同名 tools。名称必须在特定聊天请求中提供给 model 的所有 tools 中唯一。description:tool 的描述,model 可以使用它来理解何时以及如何调用 tool。如果未提供,方法名称将用作 tool 描述。但是,强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对于 model 理解 tool 的用途以及如何使用它至关重要。未能提供良好的描述可能导致 model 在应该使用时不使用 tool 或错误使用它。inputSchema:tool 输入参数的 JSON schema。如果未提供,将根据方法参数自动生成 schema。您可以使用@ToolParam注解提供有关输入参数的附加信息,例如描述或参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有输入参数都被视为必需。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 JSON Schema。
ToolMetadata.Builder 允许您构建 ToolMetadata 实例并定义 tool 的附加设置:
returnDirect:tool 结果是否应直接返回给客户端或传递回 model。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 返回直接。
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinitions.builder(method)
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.toolObject(new DateTimeTools())
.build();
方法可以是静态的或实例的,并且可以具有任何可见性(public、protected、package-private 或 private)。包含方法的类可以是顶级类或嵌套类,也可以具有任何可见性(只要在您计划实例化它的地方可以访问)。
NOTE: Spring AI 为 tool 方法的 AOT 编译提供内置支持,只要包含方法的类是 Spring bean(例如
@Component)。否则,您需要向 GraalVM 编译器提供必要的配置。例如,通过用@RegisterReflection(memberCategories = MemberCategory.INVOKE_DECLARED_METHODS)注解类。
您可以为方法定义任意数量的参数(包括无参数),支持大多数类型(基元、POJO、枚举、列表、数组、映射等)。同样,方法可以返回大多数类型,包括 void。如果方法返回值,返回类型必须是可序列化类型,因为结果将被序列化并发送回 model。
NOTE: 某些类型不受支持。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 方法 Tool 限制。
如果方法是静态的,您可以省略 toolObject() 方法,因为不需要它。
class DateTimeTools {
static String getCurrentDateTime() {
return LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
}
}
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinitions.builder(method)
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.build();
Spring AI 将自动为方法的输入参数生成 JSON schema。Schema 由 model 用于理解如何调用 tool 并准备 tool 请求。@ToolParam 注解可用于提供有关输入参数的附加信息,例如描述或�参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有输入参数都被视为必需。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
class DateTimeTools {
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
@ToolParam 注解允许您提供有关 tool 参数的关键信息:
description:参数的描述,model 可以使用它来更好地理解如何使用它。例如,参数应该是什么格式,允许什么值等。required:参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有参数都被视为必需。
如果参数用 @Nullable 注解,除非使用 @ToolParam 注解明确标记为必需,否则将被视为可选。
除了 @ToolParam 注解外,您还可以使用来自 Swagger 的 @Schema 注解或来自 Jackson 的 @JsonProperty。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 JSON Schema。
向 ChatClient 和 ChatModel 添加 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以将 MethodToolCallback 实例传递给 ChatClient 的 toolCallbacks() 方法。
Tool 仅适用于添加它的特定聊天请求。
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();
向 ChatClient 添加默认 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以通过将 MethodToolCallback 实例传递给 defaultToolCallbacks() 方法,将默认 tools 添加到 ChatClient.Builder。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在从同一
ChatClient.Builder构建的所有ChatClient实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultToolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build();
向 ChatModel 添加 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以将 MethodToolCallback 实例传递给用于调用 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 toolCallbacks() 方法。Tool 仅适用于添加它的特定聊天请求。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build():
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What day is tomorrow?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);
向 ChatModel 添加默认 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以通过将 MethodToolCallback 实例传递给用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolCallbacks() 方法,在构造时向 ChatModel 添加默认 tools。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在该
ChatModel实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请��求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build())
.build();
方法 Tool 限制
以下类型目前不支持作为用作 tools 的方法的参数或返回类型:
Optional- 异步类型(例如
CompletableFuture、Future) - 响应式类型(例如
Flow、Mono、Flux) - 函数类型(例如
Function、Supplier、Consumer)。
函数类型使用基于函数的 tool 规范方法支持。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 函数作为 Tools。
函数作为 Tools
Spring AI 提供了从函数指定 tools 的内置支持,可以使用低级 FunctionToolCallback 实现以编程方式,或作为在运行时解析的 @Bean(s) 动态指定。
编程式规范:FunctionToolCallback
您可以通过编程方式构建 FunctionToolCallback 来将函数类型(Function、Supplier、Consumer 或 BiFunction)转�换为 tool。
public class WeatherService implements Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> {
public WeatherResponse apply(WeatherRequest request) {
return new WeatherResponse(30.0, Unit.C);
}
}
public enum Unit { C, F }
public record WeatherRequest(String location, Unit unit) {}
public record WeatherResponse(double temp, Unit unit) {}
FunctionToolCallback.Builder 允许您构建 FunctionToolCallback 实例并提供有关 tool 的关键信息:
name:tool 的名称。AI model 使用此名称在调用时识别 tool。因此,不允许在同一上下文中有两个同名 tools。名称必须在特定聊天请求中提供给 model 的所有 tools 中唯一。必需。toolFunction:表示 tool 方法的函数对象(Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction)。必需。description:tool 的描述,model 可以使用它来理解何时以及如何调用 tool。如果未提供,方法名称将用作 tool 描述。但是,强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对于 model 理解 tool 的用途以及如何使用它至关重要。未能提供良好的描述可能导致 model 在应该使用时不使用 tool 或错误使用它。inputType:函数输入的类型。必需。inputSchema:tool 输入参数的 JSON schema。如果未提供,将根据inputType自动生成 schema。您可以使用@ToolParam注解提供有关输入参数的附加信息,例如描述或参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有输入参数都被视为必需。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 JSON Schema。toolMetadata:定义附加设置的ToolMetadata实例,例如结果是否应直接返回给客户端,以及要使用的结果转换器。您可以使用ToolMetadata.Builder类构建它。toolCallResultConverter:用于将 tool call 的结果转换为String对象以发送回 AI model 的ToolCallResultConverter实例。如果未提供,将使用默认转换器(DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
ToolMetadata.Builder 允许您构建 ToolMetadata 实例并定义 tool 的附加设置:
returnDirect:tool 结果是否应直接返回给客户��端或传递回 model。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 返回直接。
ToolCallback toolCallback = FunctionToolCallback
.builder("currentWeather", new WeatherService())
.description("Get the weather in location")
.inputType(WeatherRequest.class)
.build();
函数输入和输出可以是 Void 或 POJO。输入和输出 POJO 必须是可序列化的,因为结果将被序列化并发送回 model。函数以及输入和输出类型必须是 public。
NOTE: 某些类型不受支持。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 函数 Tool 限制。
向 ChatClient 添加 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给 ChatClient 的 toolCallbacks() 方法。Tool 仅适用于添加它的特定聊天请求。
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?")
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();
向 ChatClient 添加默认 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以通过将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给 defaultToolCallbacks() 方法,将默认 tools 添加到 ChatClient.Builder。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在从同一
ChatClient.Builder构建的所有ChatClient实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultToolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build();
向 ChatModel 添加 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 toolCallbacks() 方法。Tool 仅适用于添加它的特定聊天请求。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build():
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);
向 ChatModel 添加默认 Tools
使用编程式规范方法时,您可以通过将 FunctionToolCallback 实例传递给用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolCallbacks() 方法,在构造时向 ChatModel 添加默认 tools。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在该
ChatModel实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build())
.build();
动态规范:@Bean
您可以将 tools 定义为 Spring bean,并让 Spring AI 使用 ToolCallbackResolver 接口(通过 SpringBeanToolCallbackResolver 实现)在运行时动态解析它们,而不是以编程方式指定 tools。此选项使您可以使用任何 Function、Supplier、Consumer 或 BiFunction bean 作为 tool。Bean 名称将用作 tool 名称,可以使用来自 Spring Framework 的 @Description 注解为 tool 提供描述,model 使用它来理解何时以及如何调用 tool。如果您不提供描述,方法名称将用作 tool 描述。但是,强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对于 model 理解 tool 的用途以及如何使用它至关重要。未能提供良好的描述可能导致 model 在应该使用时不使用 tool 或错误使用它。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class WeatherTools {
WeatherService weatherService = new WeatherService();
@Bean
@Description("Get the weather in location")
Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> currentWeather() {
return weatherService;
}
}
NOTE: 某些类型不受支持。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 函数 Tool 限制。
Tool 输入参数的 JSON schema 将自动生成。您可以使用 @ToolParam 注解提供有关输入参数的附加信息,例如描述或参数是必需还是可选的。默认情况下,所有输入参数都被视为必需。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 JSON Schema。
record WeatherRequest(@ToolParam(description = "The name of a city or a country") String location, Unit unit) {}
此 tool 规范方法的缺点是不保证类型安全,因为 tool 解析是在运行时完成的。为了缓解这种情况,您可以使用 @Bean 注解显式指定 tool 名称并将值存储在常量中,以便您可以在聊天请求中使用它而不是硬编码 tool 名称。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class WeatherTools {
public static final String CURRENT_WEATHER_TOOL = "currentWeather";
@Bean(CURRENT_WEATHER_TOOL)
@Description("Get the weather in location")
Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> currentWeather() {
...
}
}
向 ChatClient 添加 Tools
使用动态规范方法时,您可以将 tool 名称(即函数 bean 名称)传递给 ChatClient 的 toolNames() 方法。
Tool 仅适用于添加它的特定聊天请求。
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?")
.toolNames("currentWeather")
.call()
.content();
向 ChatClient 添加默认 Tools
使用动态规范方法时,您可以通过将 tool 名称传递给 defaultToolNames() 方法,将默认 tools 添加到 ChatClient.Builder。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在从同一
ChatClient.Builder构建的所有ChatClient实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultToolNames("currentWeather")
.build();
向 ChatModel 添加 Tools
使用动态规范方法时,您可以将 tool 名称传递给用于调用 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 toolNames() 方法。Tool 仅适用于添加它的特定聊天请求。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolNames("currentWeather")
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);
向 ChatModel 添加默认 Tools
使用动态规范方法时,您可以通过将 tool 名称传递给用于创建 ChatModel 的 ToolCallingChatOptions 实例的 toolNames() 方法,在构造时向 ChatModel 添加默认 tools。
如果同时提供了默认和运行时 tools,运行时 tools 将完全覆盖默认 tools。
WARNING: 默认 tools 在该
ChatModel实例执行的所有聊天请求之间共享。它们对于在不同聊天请求之间常用的 tools 很有用,但如果使用不当也可能很危险,可能会在不应使用时使它们可用。
ChatModel chatModel = OllamaChatModel.builder()
.ollamaApi(OllamaApi.builder().build())
.defaultOptions(ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolNames("currentWeather")
.build())
.build();
函数 Tool 限制
以下类型目前不支持作为用作 tools 的函数的输入或输出类型:
- 基元类型
Optional- 集合类型(例如
List、Map、Array、Set) - 异步类型(例如
CompletableFuture、Future) - 响应式类型(例如
Flow、Mono、Flux)。
基元类型和集合使用基于方法的 tool 规范方法支持。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 方法作为 Tools。
Tool 规范
在 Spring AI 中,tools 通过 ToolCallback 接口建模。在前面的部分中,我们已经看到了如何使用 Spring AI 提供的内置支持从方法和函数定义 tools(请参阅 方法作为 Tools 和 函数作为 Tools)。本节将更深入地介绍 tool 规范以及如何自定义和扩展它以支持更多用例。
Tool Callback
ToolCallback 接口提供了一种定义可由 AI model 调用的 tool 的方法,包括定义和执行逻辑。当您想从头开始定义 tool 时,这是要实现的主要接口。例如,您可以从 MCP Client(使用 Model Context Protocol)或 ChatClient(构建模块化 agentic 应用程序)定义 ToolCallback。
接口提供以下方法:
public interface ToolCallback {
/**
* Definition used by the AI model to determine when and how to call the tool.
*/
ToolDefinition getToolDefinition();
/**
* Metadata providing additional information on how to handle the tool.
*/
ToolMetadata getToolMetadata();
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and return the result to send back to the AI model.
*/
String call(String toolInput);
/**
* Execute tool with the given input and context, and return the result to send back to the AI model.
*/
String call(String toolInput, ToolContext tooContext);
}
Spring AI 为 tool 方法(MethodToolCallback)和 tool 函数(FunctionToolCallback)提供内置实现。
Tool Definition
ToolDefinition 接口提供 AI model 了解 tool 可用性所需的信息,包括 tool 名称、描述和输入 schema。每个 ToolCallback 实现必须提供 ToolDefinition 实例来定义 tool。
接口提供以下方法:
public interface ToolDefinition {
/**
* The tool name. Unique within the tool set provided to a model.
*/
String name();
/**
* The tool description, used by the AI model to determine what the tool does.
*/
String description();
/**
* The schema of the parameters used to call the tool.
*/
String inputSchema();
}
NOTE: 有关输入 schema 的更多详细信息,请参阅 JSON Schema。
ToolDefinition.Builder 允许您使用默认实现(DefaultToolDefinition)构建 ToolDefinition 实例。
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder()
.name("currentWeather")
.description("Get the weather in location")
.inputSchema("""
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["C", "F"]
}
},
"required": ["location", "unit"]
}
""")
.build();
方法 Tool Definition
从方法构建 tools 时,ToolDefinition 会自动为您生成。如果您希望自己生成 ToolDefinition,可以使用此便捷构建器。
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinitions.from(method);
从方法生成的 ToolDefinition 包括方法名称作为 tool 名称、方法名称作为 tool 描述,以及方法输入参数的 JSON schema。如果方法用 @Tool 注解,tool 名称和描述将从注解中获取(如果已设置)。
NOTE: 有关更多详细信息,请参阅 方法作为 Tools。
如果您希望显式提供部分或全部属性,可以使用 ToolDefinition.Builder 构建自定义 ToolDefinition 实例。
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinitions.builder(method)
.name("currentDateTime")
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.inputSchema(JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForMethodInput(method))
.build();
函数 Tool Definition
从函数构建 tools 时,ToolDefinition 会自动为您生成。当您使用 FunctionToolCallback.Builder 构建 FunctionToolCallback 实例时,可以提供将用于生成 ToolDefinition 的 tool 名称、描述和输入 schema。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 函数作为 Tools。
JSON Schema
向 AI model 提供 tool 时,model 需要知道调用 tool 的输入类型的 schema。Schema 用于理解如何调用 tool 并准备 tool 请求。Spring AI 通过 JsonSchemaGenerator 类为生成 tool 输入类型的 JSON Schema 提供内置支持。Schema 作为 ToolDefinition 的一部分提供。
NOTE: 有关
ToolDefinition以及如何将输入 schema 传递给它的更多详细信息,请参阅 Tool Definition。
JsonSchemaGenerator 类在底层用于为方法或函数的输入参数生成 JSON schema,使用 方法作为 Tools 和 函数作为 Tools 中描述的任何策略。JSON schema 生成逻辑支持一系列注解,您可以在方法和函数的输入参数上使用这些注解来自定义生成的 schema。
本节描述在生成 tool 输入参数的 JSON schema 时可以自定义的两个主要选项:描述和必需状态。
描述
除了为 tool 本身提供描述外,您还可以为 tool 的输入参数提供描述。描述可用于提供有关输入参数的关键信息,例如参数应该是什么格式、允许什么值等。这对于帮助 model 理解输入 schema 以及如何使用它很有用。Spring AI 使用以下注解之一为输入参数生成描述提供内置支持:
- Spring AI 的
@ToolParam(description = "...") - Jackson 的
@JsonClassDescription(description = "...") - Jackson 的
@JsonPropertyDescription(description = "...") - Swagger 的
@Schema(description = "...")。
此方法适用于方法和函数,并且可以递归地用于嵌套类型。
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.Tool;
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format") String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
必需/可选
默认情况下,每个输入参数都被视为必需,这强制 AI model 在调用 tool 时为其提供值。但是,您可以使用以下注解之一使输入参数可选,按此优先级顺序:
- Spring AI 的
@ToolParam(required = false) - Jackson 的
@JsonProperty(required = false) - Swagger 的
@Schema(required = false) - Spring Framework 的
@Nullable。
此方法适用于方法和函数,并且可以递归地用于嵌套类型。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Update customer information")
void updateCustomerInfo(Long id, String name, @ToolParam(required = false) String email) {
System.out.println("Updated info for customer with id: " + id);
}
}
WARNING: 为输入参数定义正确的必需状态对于减轻幻觉风险并确保 model 在调用 tool 时提供正确的输入至关重要。在前面的示例中,
结果转换
Tool call 的结果使用 ToolCallResultConverter 序列化,然后发送回 AI model。ToolCallResultConverter 接口提供了一种将 tool call 的结果转换为 String 对象的方法。
接口提供以下方法:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolCallResultConverter {
/**
* Given an Object returned by a tool, convert it to a String compatible with the
* given class type.
*/
String convert(@Nullable Object result, @Nullable Type returnType);
}
结果必须是可序列化类型。默认情况下,结果使用 Jackson(DefaultToolCallResultConverter)序列化为 JSON,但您可以通过提供自己的 ToolCallResultConverter 实现来自定义序列化过程。
Spring AI 在方法和函数 tools 中都依赖 ToolCallResultConverter。
方法 Tool Call 结果转换
使用声明式方法从方法构建 tools 时,您可以通过设置 @Tool 注解的 resultConverter() 属性来为 tool 提供自定义 ToolCallResultConverter。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information", resultConverter = CustomToolCallResultConverter.class)
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id) {
return customerRepository.findById(id);
}
}
如果使用编程式方法,您可以通过设置 MethodToolCallback.Builder 的 resultConverter() 属性来为 tool 提供自定义 ToolCallResultConverter。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 方法作为 Tools。
函数 Tool Call 结果转换
使用编程式方法从函数��构建 tools 时,您可以通过设置 FunctionToolCallback.Builder 的 resultConverter() 属性来为 tool 提供自定义 ToolCallResultConverter。
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 函数作为 Tools。
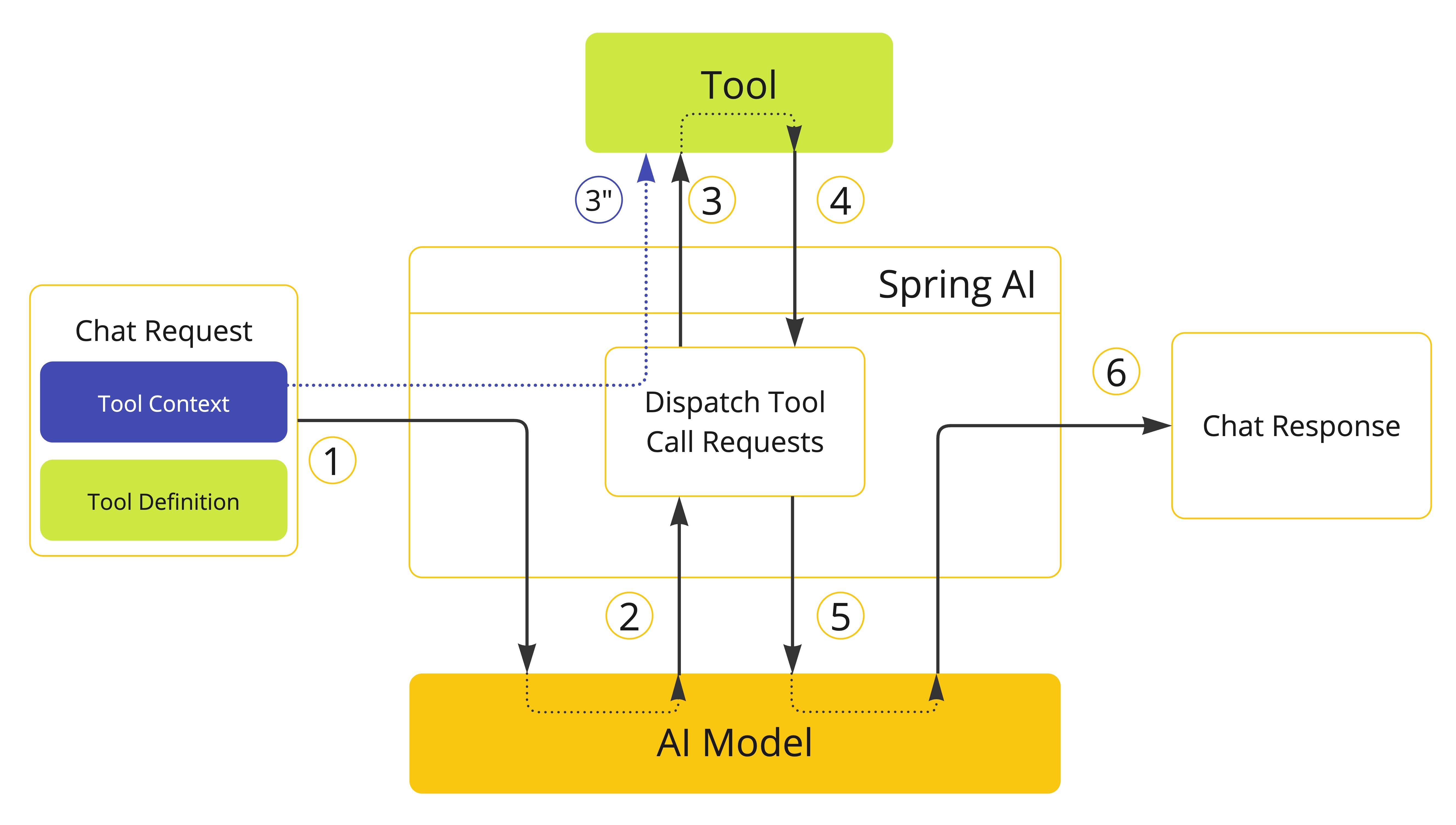
Tool Context
Spring AI 支持通过 ToolContext API 向 tools 传递附加的上下文信息。此功能允许您提供额外的、用户提供的数据,这些数据可以在 tool 执行期间与 AI model 传递的 tool 参数一起使用。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information")
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id, ToolContext toolContext) {
return customerRepository.findById(id, toolContext.getContext().get("tenantId"));
}
}
ToolContext 由用户在调用 ChatClient 时提供的数据填充。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42")
.tools(new CustomerTools())
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);
NOTE:
ToolContext中提供的任何数据都不会发送到 AI model。
同样,您可以在直接调用 ChatModel 时定义 tool 上下文数据。
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback[] customerTools = ToolCallbacks.from(new CustomerTools());
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(customerTools)
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42", chatOptions);
chatModel.call(prompt);
如果 toolContext 选项在默认选项和运行时选项中都有设置,生成的 ToolContext 将是两者的合并,
其中运行时选项优先于默认选项。
返回直接
默认情况下,tool call 的结果作为响应发送回 model。然后,model 可以使用结果继续对话。
在某些情况下,您可能希望将结果直接返回给调用者,而不是将其发送回 model。例如,如果您构建一个依赖 RAG tool 的 agent,您可能希望将结果直接返回给调用者,而不是将其发送回 model 进行不必要的后处理。或者,您可能有某些 tools 应该结束 agent 的推理循环。
每个 ToolCallback 实现可以定义 tool call 的结果是否应直接返回给调用者或发送回 model。默认情况下,结果发送回 model。但您可以按 tool 更改此行为。
负责管理 tool 执行生命周期的 ToolCallingManager 负责处理与 tool 关联的 returnDirect 属性。如果属性设置为 true,tool call 的结果将直接返回给调用者。否则,结果将发送回 model。
NOTE: 如果同时请求多个 tool calls,所有 tools 的
returnDirect属性必须设置为true才能将结果直接返回给调用者。否则,结果将发送回 model。
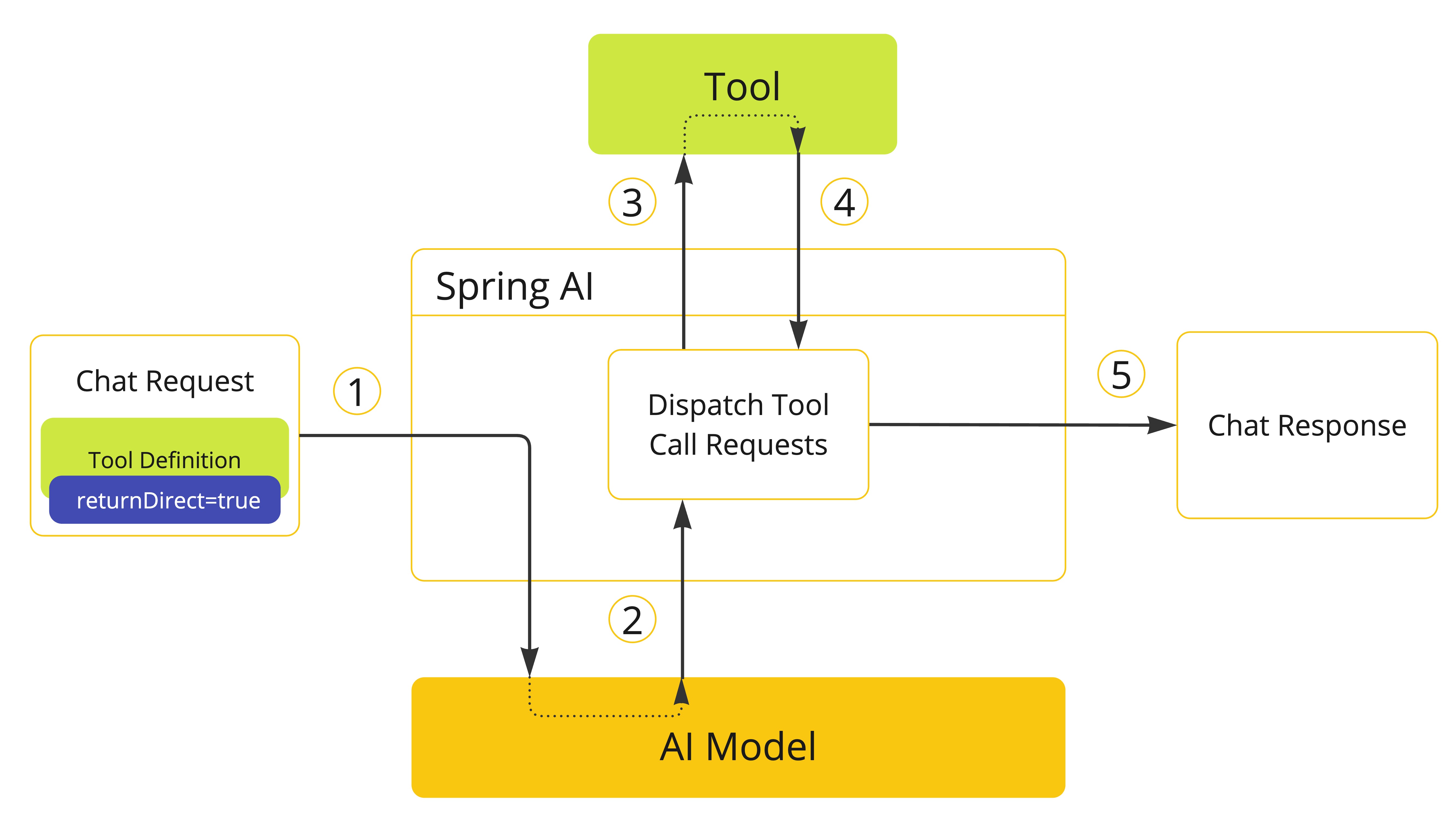
- 当我们想要使 tool 可用于 model 时,我们在聊天请求中包含其定义。如果我们希望 tool 执行的结果直接返回给调用者,我们将
returnDirect属性设置为true。 - 当 model 决定调用 tool 时,它发送带有 tool 名称和根据定义 schema 建模的输入参数的响应。
- 应用程序负责使用 tool 名称来识别并使用提供的输入参数执行 tool。
- Tool call 的结果由应用程序处理。
- 应用程序将 tool call 结果直接发送给调用者,而不是将其发送回 model。
方法返回直接
使用声明式方法从方法构建 tools 时,您可以通过将 @Tool 注解的 returnDirect 属性设置为 true 来标记 tool 将结果直接返回给调用者。
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information", returnDirect = true)
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id) {
return customerRepository.findById(id);
}
}
如果使用编程式方法,您可以通过 ToolMetadata 接口设置 returnDirect 属性,并将其传递给 MethodToolCallback.Builder。
ToolMetadata toolMetadata = ToolMetadata.builder()
.returnDirect(true)
.build();
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 方法作为 Tools。
函数返回直接
使用编程式方法从函数构建 tools 时,您可以通过 ToolMetadata 接口设置 returnDirect 属性,并�将其传递给 FunctionToolCallback.Builder。
ToolMetadata toolMetadata = ToolMetadata.builder()
.returnDirect(true)
.build();
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 函数作为 Tools。
Tool 执行
Tool 执行是使用提供的输入参数调用 tool 并返回结果的过程。Tool 执行由 ToolCallingManager 接口处理,该接口负责管理 tool 执行生命周期。
public interface ToolCallingManager {
/**
* Resolve the tool definitions from the model's tool calling options.
*/
List<ToolDefinition> resolveToolDefinitions(ToolCallingChatOptions chatOptions);
/**
* Execute the tool calls requested by the model.
*/
ToolExecutionResult executeToolCalls(Prompt prompt, ChatResponse chatResponse);
}
如果您使用任何 Spring AI Spring Boot Starters,DefaultToolCallingManager 是 ToolCallingManager 接口的自动配置实现。您可以通过提供自己的 ToolCallingManager bean 来自定义 tool 执行行为。
@Bean
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager() {
return ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
}
默认情况下,Spring AI 在每个 ChatModel 实现内部透明地为您管理 tool 执行生命周期。但您可以选择退出此行为并自己控制 tool 执行。本节描述这两种场景。
框架控制的 Tool 执行
使用默认行为时,Spring AI 将自动拦截来自 model 的任何 tool call 请求,调用 tool 并将结果返回给 model。所有这些都由每个使用 ToolCallingManager 的 ChatModel 实现透明地为您完成。
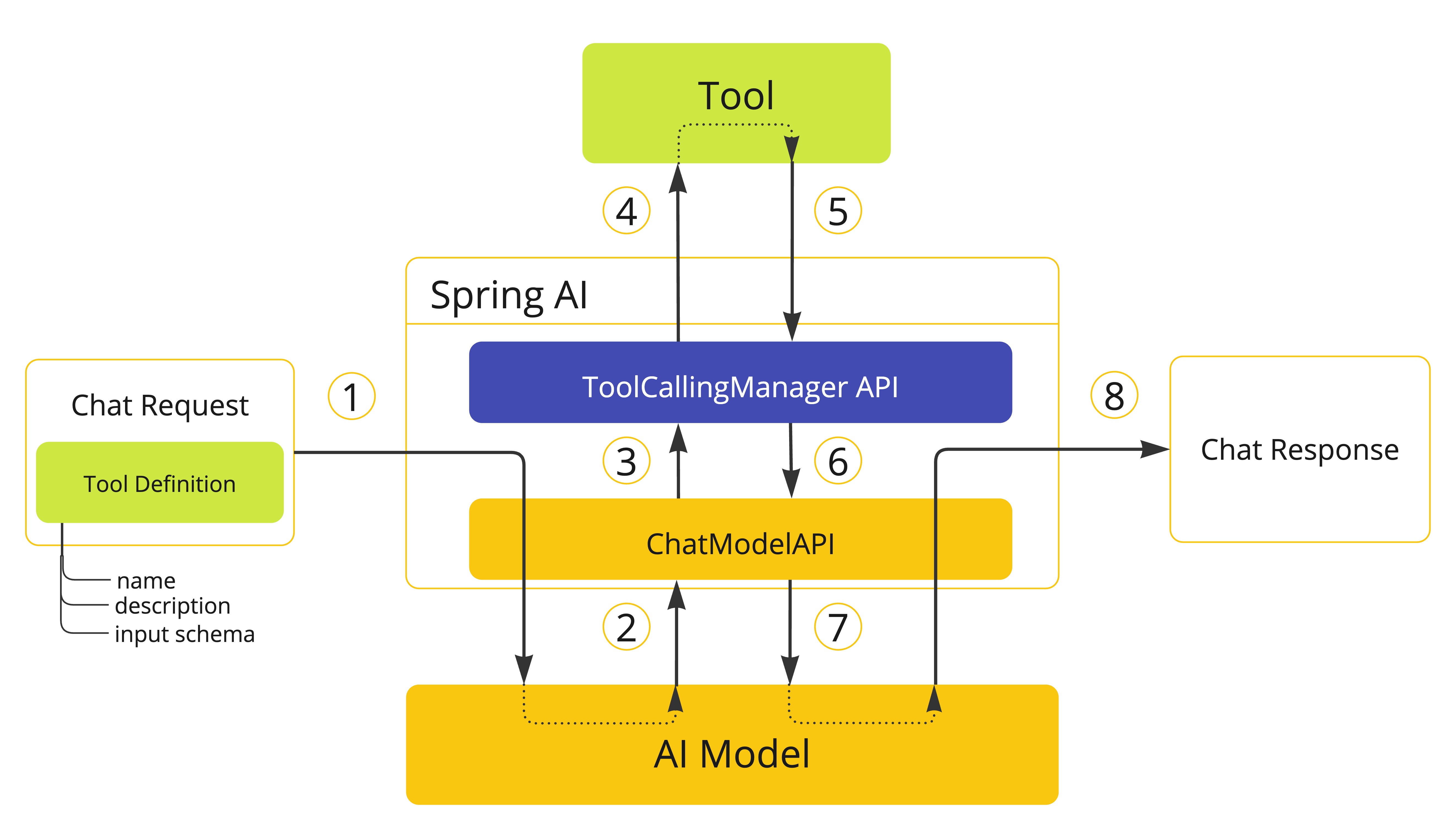
- 当我们想要使 tool 可用于 model 时,我们在聊天请求(
Prompt)中包含其定义,并调用将请求发送到 AI model 的ChatModelAPI。 - 当 model 决定调用 tool 时,它发送带有 tool 名称和根据定义 schema 建模的输入参数的响应(
ChatResponse)。 ChatModel将 tool call 请求发送到ToolCallingManagerAPI。ToolCallingManager负责识别要调用的 tool 并使用提供的输入参数执行它。- Tool call 的结果返回到
ToolCallingManager。 ToolCallingManager将 tool 执行结果返回给ChatModel。ChatModel将 tool 执行结果发送回 AI model(ToolResponseMessage)。- AI model 使用 tool call 结果作为附加上下文生成最终响应,并通过
ChatClient将其发送回调用者(ChatResponse)。
WARNING: 目前,与 model 交换的关于 tool 执行的内部消息不会暴露给用户。如果您需要访问这些消息,应该使用用户控制的 tool 执行方法。
确定 tool call 是否有资格执行的逻辑由 ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate 接口处理。默认情况下,tool 执行资格通过检查 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 internalToolExecutionEnabled 属性是否设置为 true(默认值),以及 ChatResponse 是否包含任何 tool calls 来确定。
public class DefaultToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate implements ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate {
@Override
public boolean test(ChatOptions promptOptions, ChatResponse chatResponse) {
return ToolCallingChatOptions.isInternalToolExecutionEnabled(promptOptions) && chatResponse != null
&& chatResponse.hasToolCalls();
}
}
您可以在创建 ChatModel bean 时提供 ToolExecutionEligibilityPredicate 的自定义实现。
用户控制的 Tool 执行
在某些情况下,您可能希望自己控制 tool 执行生命周期。您可以通过将 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 internalToolExecutionEnabled 属性设置为 false 来执行此操作。
当您使用此选项调用 ChatModel 时,tool 执行将委托给调用者,让您完全控制 tool 执行生命周期。您有责任检查 ChatResponse 中的 tool calls 并使用 ToolCallingManager 执行它们。
以下示例演示了用户控制的 tool 执行方法的最小实现:
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager = ToolCallingManager.builder().build();
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(new CustomerTools())
.internalToolExecutionEnabled(false)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42", chatOptions);
ChatResponse chatResponse = chatModel.call(prompt);
while (chatResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(prompt, chatResponse);
prompt = new Prompt(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory(), chatOptions);
chatResponse = chatModel.call(prompt);
}
System.out.println(chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getText());
NOTE: 选择用户控制的 tool 执行方法时,我们建议使用
ToolCallingManager来管理 tool calling 操作。这样,您可以受益于 Spring AI 为 tool 执行提供的内置支持。但是,没有什么可以阻止您实现自己的 tool 执行逻辑。
下一个示例显示了用户控制的 tool 执行方法的最小实现,结合了 ChatMemory API 的使用:
ToolCallingManager toolCallingManager = DefaultToolCallingManager.builder().build();
ChatMemory chatMemory = MessageWindowChatMemory.builder().build();
String conversationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
ChatOptions chatOptions = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(ToolCallbacks.from(new MathTools()))
.internalToolExecutionEnabled(false)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(
List.of(new SystemMessage("You are a helpful assistant."), new UserMessage("What is 6 * 8?")),
chatOptions);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, prompt.getInstructions());
Prompt promptWithMemory = new Prompt(chatMemory.get(conversationId), chatOptions);
ChatResponse chatResponse = chatModel.call(promptWithMemory);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, chatResponse.getResult().getOutput());
while (chatResponse.hasToolCalls()) {
ToolExecutionResult toolExecutionResult = toolCallingManager.executeToolCalls(promptWithMemory,
chatResponse);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory()
.get(toolExecutionResult.conversationHistory().size() - 1));
promptWithMemory = new Prompt(chatMemory.get(conversationId), chatOptions);
chatResponse = chatModel.call(promptWithMemory);
chatMemory.add(conversationId, chatResponse.getResult().getOutput());
}
UserMessage newUserMessage = new UserMessage("What did I ask you earlier?");
chatMemory.add(conversationId, newUserMessage);
ChatResponse newResponse = chatModel.call(new Prompt(chatMemory.get(conversationId)));
异常处理
当 tool call 失败时,异常作为 ToolExecutionException 传播,可以捕获以处理错误。
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 可用于处理 ToolExecutionException,有两种结果:要么生成要发送回 AI model 的错误消息,要么抛出异常供调用者处理。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor {
/**
* Convert an exception thrown by a tool to a String that can be sent back to the AI
* model or throw an exception to be handled by the caller.
*/
String process(ToolExecutionException exception);
}
如果您使用任何 Spring AI Spring Boot Starters,DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 是 ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 接口的自动配置实现。默认情况下,RuntimeException 的错误消息会发送回 model,而检查异常和错误(例如,IOException、OutOfMemoryError)总是被抛出。DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 构造函数允许您将 alwaysThrow 属性设置为 true 或 false。如果为 true,将抛出异常而不是将错误消息发送回 model。
您可以使用 spring.ai.tools.throw-exception-on-error 属性来控制 DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor bean 的行为:
| 属性 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
spring.ai.tools.throw-exception-on-error | 如果为 true,tool calling 错误将作为异常抛出供调用者处理。如果为 false,错误将转换为消息并发送回 AI model,允许它处理并响应错误。 | false |
@Bean
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor toolExecutionExceptionProcessor() {
return new DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor(true);
}
NOTE: 如果您定义了自己的
ToolCallback实现,请确保在call()方法中作为 tool 执行逻辑的一部分发生错误时抛出ToolExecutionException。
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor 由默认 ToolCallingManager(DefaultToolCallingManager)内部使用,以处理 tool 执行期间的异常。有关 tool 执行生命周期的更多详细信息,请参阅 Tool 执行。
Tool 解析
向 model 传递 tools 的主要方法是在调用 ChatClient 或 ChatModel 时提供 ToolCallback(s),
使用 方法作为 Tools 和 函数作为 Tools 中描述的策略之一。
但是,Spring AI 还支持使用 ToolCallbackResolver 接口在运行时动态解析 tools。
public interface ToolCallbackResolver {
/**
* Resolve the {@link ToolCallback} for the given tool name.
*/
@Nullable
ToolCallback resolve(String toolName);
}
使用此方法时:
- 在客户端,您向
ChatClient或ChatModel提供 tool 名称,而不是ToolCallback(s)。 - 在服务器端,
ToolCallbackResolver实现负责将 tool 名称解析为相应的ToolCallback实例。
默认情况下,Spring AI 依赖于 DelegatingToolCallbackResolver,它将 tool 解析委托给 ToolCallbackResolver 实例列表:
SpringBeanToolCallbackResolver从类型为Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction的 Spring bean 解析 tools。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 动态规范 Bean。StaticToolCallbackResolver从ToolCallback实例的静态列表解析 tools。使用 Spring Boot 自动配置时,此解析器会自动配置应用程序上下文中定义的所有类型为ToolCallback的 bean。
如果您依赖 Spring Boot 自动配置,可以通过提供自定义 ToolCallbackResolver bean 来自定义解析逻辑。
@Bean
ToolCallbackResolver toolCallbackResolver(List<FunctionCallback> toolCallbacks) {
StaticToolCallbackResolver staticToolCallbackResolver = new StaticToolCallbackResolver(toolCallbacks);
return new DelegatingToolCallbackResolver(List.of(staticToolCallbackResolver));
}
ToolCallbackResolver 由 ToolCallingManager 内部使用,以在运行时动态解析 tools,支持 框架控制的 Tool 执行 和 用户控制的 Tool 执行。
可观测性
Tool calling 包括可观测性支持,使用 spring.ai.tool 观察来测量完成时间并传播跟踪信息。请参阅 Tool Calling 可观测性。
可选地,Spring AI 可以将 tool call 参数和结果导出为 span 属性,默认情况下出于敏感性原因禁用。详细信息:Tool Call 参数和结果数据。
日志记录
Tool calling 功能的所有主要操作都在 DEBUG 级别记录。您可以通过将 org.springframework.ai 包的日志级别设置为 DEBUG 来启用日志记录。